Table of Contents
- Introduction to Virtual Private Networks (VPNs)
- Why the Transition from VPN to ZTNA Is Gaining Momentum?
- Challenges Faced When Implementing ZTNA
- ZTNA Best Practices and Deployment Strategies
- Future of Cybersecurity: ZTNA as a Standard
- Comparative Analysis: VPN and ZTNA in the Modern Threat Landscape
- User Education and Awareness: Key to ZTNA Adoption
- Conclusion: The Path to a More Secure Digital Environment
Key Takeaways
- Understanding the origin and limitations of VPNs
- Exploring the principles and advantages of ZTNA
- Recognizing the drivers of transition from VPN to ZTNA
- Identifying challenges of adopting ZTNA and ways to overcome them
- Learning best practices for smooth ZTNA deployment
- Anticipating the future of cybersecurity and its shift towards ZTNA
1. Introduction to Virtual Private Networks (VPNs)
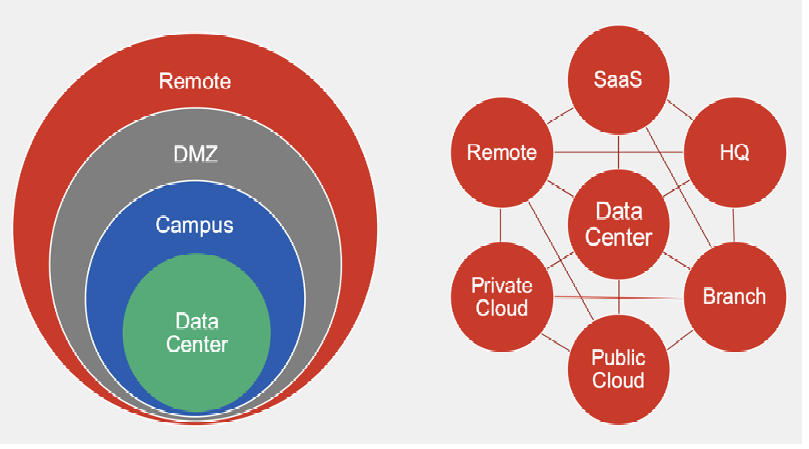
VPNs have been used in the digital world to ensure cybersecurity by creating a secure connection between a user’s device and the network. However, they need to be more sufficient in addressing insider threats and have limited visibility over user activity.
The Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA) model offers an alternative to traditional VPNs, prioritizing continuous verification and granular access control. It represents a fundamental shift in cybersecurity philosophy from broad network access to a more restricted, secure, and user-specific access methodology.
2. Why the Transition from VPN to ZTNA Is Gaining Momentum?
As the rate of digital transformation accelerates, the transition from ZTNA versus VPN is gaining substantial momentum. A growing number of organizations recognize the inadequacies of VPNs in protecting an increasingly distributed workforce and the proliferation of cloud-based assets.
The versatility of ZTNA in facilitating secure remote access while simultaneously delivering stringent cybersecurity renders it an invaluable tool for modern businesses. More significantly, ZTNA aligns with current data protection mandates, providing the level of security expected by regulatory standards.
Under ZTNA, access decisions are made dynamically based on real-time user, device, and access environment risk analysis. This is crucial given the sophisticated nature of contemporary cyber threats. By implementing ZTNA, companies can rest assured that their data is safeguarded with resilient state-of-the-art security in the face of rapidly evolving attack vectors.
3. Challenges Faced When Implementing ZTNA
While the benefits of ZTNA are clear, adopting this model comes with challenges. Organizations transitioning to ZTNA may grapple with issues such as legacy infrastructure incompatibilities, a lack of in-house expertise, and the potential for significant upfront costs. Resistance to change is a common obstacle, as stakeholders may need to be more open to familiar VPN solutions.
To navigate these hurdles, businesses must develop a comprehensive strategy considering technical prerequisites, potential impacts on user experience, and staff training needs. A phased introduction can mitigate operational disruptions and allow for the iterative refinement of access policies.
Effectively communicating the long-term advantages of ZTNA can also pave the way for smoother organizational buy-in. The article further examines challenges in implementing ZTNA, highlighting the importance of overcoming budget constraints and expertise shortages to realize a Zero Trust environment.
4. ZTNA Best Practices and Deployment Strategies
Effective implementation of ZTNA demands adherence to several best practices. Firstly, organizations should comprehensively audit their current security posture and access requirements. Detailed planning encompassing stakeholder concerns and potential security risks can establish a solid foundation for a successful ZTNA transition.
Tailored policies that mandate strict identity verification and context-aware access must be developed. A staged rollout allows for fine-tuning these policies while providing an opportunity for end-user feedback.
Integrating user and entity behavior analytics (UEBA) systems can significantly enhance the ability to identify suspicious patterns and potentially malicious activities. By investing in advanced access control measures and ensuring the scalability of solutions, organizations can future-proof their cybersecurity framework against increasingly complex cybersecurity threats.
5. Future of Cybersecurity: ZTNA as a Standard
Forecasting the progression of cybersecurity, it becomes evident that ZTNA is set to play a central role in the future security architecture of organizations. The decentralization of the workforce and the rise of cloud computing demand a transition to security models that can continuously ensure the integrity and confidentiality of data, irrespective of user location or device.
What stands out is the surge in the ZTNA market and the consistent advancements and refinements it has undergone. These ongoing developments promise to deliver user-friendly and easily manageable cybersecurity solutions that seamlessly integrate with existing IT ecosystems.
6. Comparative Analysis: VPN and ZTNA in the Modern Threat Landscape
A deeper dive into the performance of VPN and ZTNA solutions against contemporary cybersecurity threats reveals a stark contrast. VPNs, while still a viable solution for specific scenarios, are now considered less effective due to their broad trust model and inflexible access controls.
In contrast, a granular and dynamic approach to cybersecurity provides a formidable defense mechanism better equipped to mitigate the advancing risks associated with modern cybercrime.
These innovative security protocols extend protection beyond the initial point of access, continuously verifying trust throughout a session, thus minimizing exposure to potential breaches. Such an adaptive security framework ensures organizations remain vigilant against the evolving threat landscape, safeguarding their digital assets more effectively.
7. User Education and Awareness: Key to ZTNA Adoption
Educating and raising user awareness are crucial but often undervalued elements for successfully adopting ZTNA. Users form the front line of cybersecurity; thus, their understanding of security principles and protocols is paramount. By fostering a culture of cyber awareness, organizations can enable personnel to recognize and respond to security incidents swiftly.
Training programs tailored to the intricacies of ZTNA can illuminate its necessity and functionality, thereby increasing adherence to security policies and minimizing accidental insider threats. Regular updates on security best practices and an open avenue for feedback can boost the organization’s overall security literacy and, by extension, its cyber resilience.
8. Conclusion: The Path to a More Secure Digital Environment
To conclude, we stand at a pivotal point in the evolution of cybersecurity. ZTNA is poised to supersede VPNs as the de facto standard for network access security, driven by its alignment with the needs of today’s fluid and risk-intensive digital environment.
By focusing on continual trust verification and leveraging a user-centric approach, ZTNA offers a robust response to modern cyber threats. As organizations transition to a zero-trust architecture, the path to a more secure digital future becomes increasingly apparent.
The integration of ZTNA into cybersecurity strategies is not merely a trend but a strategic move toward fortifying digital infrastructures against the sophisticated threat landscape of tomorrow.